The IP address 127.0.0.1:49342 is crucial in networking. If you’re venturing into web development, system administration, or just trying to understand networking basics, you’ve likely come across these terms. The IP address 127.0.0.1, also known as localhost, is the standard address used to refer to the local machine—the computer you’re currently working on. Meanwhile, ports like 49342 serve as gateways for specific types of communication. Together, they enable smooth communication between local services, aiding in testing and development.
What is 127.0.0.1?
127.0.0.1 is referred to as localhost, which is a loopback address. When you send a request to 127.0.0.1, you send it to your computer, not across the network. This feature is immensely useful in software development and testing. When working on a project, such as a web server or an application, you can use 127.0.0.1 to test your service locally before deploying it to a public server.
Exploring Port 49342
Ports are virtual locations where different services communicate. Every IP address has many ports, each serving a distinct function. Port 49342 is one such entry point that enables programs on your computer to communicate with each other or external networks. Think of it as a phone extension; while the IP address represents the overall location, the port specifies the particular service or program. Port 49342 is often used for internal development and testing processes.
Why Use 127.0.0.1 and Port 49342 Together?
When working with applications locally, developers need a reliable way to test the communication between services. 127.0.0.1 serves as the local address, and port 49342 allows a specific application to be accessed on that address. This combination is popular in development environments where real-world interactions need to be simulated.
How 127.0.0.1:49342 Works

When an application on your local machine sends data to 127.0.0.1:49342, it uses the loopback mechanism. Essentially, instead of the data on the internet, it is directed back to your computer, specifically to the port you’ve designated (49342). This allows you to check if a service functions correctly without needing external internet connections.
Security Implications of Using 127.0.0.1:49342
Although 127.0.0.1 is safe for local testing, it’s essential to ensure that ports like 49342 are adequately secured. Sometimes, applications running on localhost may have vulnerabilities that can be exploited if mistakenly exposed to external networks. To avoid this, it’s crucial to implement firewall rules that restrict unwanted access and ensure that only trusted programs can communicate via specific ports.
Configuring Your System to Use 127.0.0.1:49342
To set up your system to use 127.0.0.1:49342, start by configuring your application to listen to this IP address and port. In most programming environments, this requires specifying the loopback IP (127.0.0.1) and the port number (49342) in your code. Afterward, you can access the service through your browser or terminal using the address “127.0.0.1:49342.”
Troubleshooting Issues with 127.0.0.1:49342
Common problems arise when a service refuses to connect to the port or multiple applications attempt to use the same port. In such cases, verifying the port’s availability and checking firewall settings are the first steps in resolving these issues. Developers may also encounter permission problems, which can be addressed by running services with the proper administrative privileges.
Best Practices for Using 127.0.0.1:49342
Always limit the number of services running on the same port to ensure security and efficiency. Log traffic to detect potential misuse. Avoid exposing 127.0.0.1:49342 to external networks unless necessary, and ensure your applications are patched to prevent exploitation.
Difference Between Localhost and Public IP
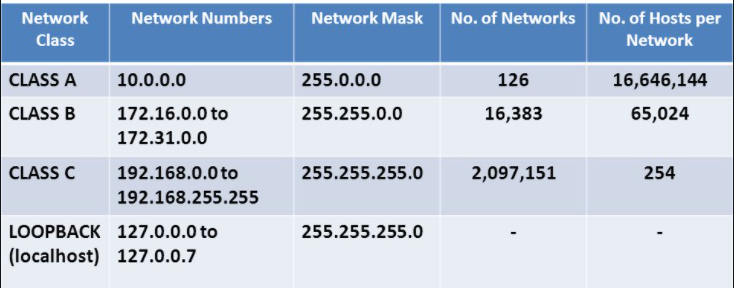
A critical difference between 127.0.0.1 and a public IP address is accessibility. While localhost is confined to your machine, public IP addresses allow communication over the internet. This distinction is vital when developing locally and deciding when to expose services publicly.
FAQs About 127.0.0.1:49342
1. What is 127.0.0.1?
127.0.0.1 is the localhost IP address, which refers to the computer used.
2. What is a port in networking?
A port is a gateway used to handle specific types of communication on a network.
3. Can I use 127.0.0.1 for testing applications?
Yes, it’s widely used in development to test local applications.
4. What does port 49342 do?
Port 49342 is a virtual point used to direct communication for specific programs.
5. How do I secure 127.0.0.1:49342?
Use firewalls and restrict access to ensure only authorized programs use this combination.
6. Why are localhost and ports used together?
They work together to route local communication within the system for testing and development.
Conclusion
Understanding 127.0.0.1:49342 is essential for developers and network administrators. This loopback IP and port combination enables secure and efficient local testing. By adhering to best practices and addressing security concerns, you can maximize the effectiveness 127.0.0.1:49342 in your development workflow.